Which of the Following Applies to Where a Managerial Accounting System Can Be Useful?
Bookkeeping as a Tool for Managers
3 Distinguish betwixt Financial and Managerial Accounting
Now that y'all have a basic understanding of managerial accounting, consider how it is similar to and different from financial accounting. After completing a fiscal accounting course, many students practice non look forward to another semester of debits, credits, and journal entries. Thankfully, managerial accounting is much different from financial accounting. Too known as management bookkeeping or cost accounting, managerial accounting provides data to managers and other users within the company in order to make more informed decisions. The overriding roles of managers (planning, controlling, and evaluating) lead to the distinction between fiscal and managerial accounting. The main objective of management accounting is to provide useful information to managers to assist them in the planning, decision-making, and evaluating roles.
Unlike managerial accounting, financial accounting is governed by rules set up out past the Fiscal Accounting Standards Lath (FASB), an independent board made upward of accounting professionals who determine and publicize the standards of fiscal bookkeeping and reporting in the United States. Larger, publicly traded companies are likewise governed by the US Securities and Commutation Commission (SEC), in the form of the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), the common ready of rules, standards, and procedures that publicly traded companies must follow when they are composing their financial statements.
Financial accounting provides information to enable stockholders, creditors, and other stakeholders to make informed decisions. This information can exist used to evaluate and make decisions for an individual company or to compare two or more companies. Withal, the information provided past fiscal accounting is primarily historical and therefore is non sufficient and is often synthesized too tardily to be overly useful to direction. Managerial bookkeeping has a more specific focus, and the information is more detailed and timelier. Managerial accounting is not governed by GAAP, so there is unending flexibility in the types of reports and information gathered. Managerial accountants regularly summate and manage "what-if" scenarios to help managers make decisions and program for future business needs. Thus, managerial accounting focuses more than on the future, while financial accounting focuses on reporting what has already happened. In addition, managerial accounting uses nonfinancial data, whereas financial accounting relies solely on financial information.
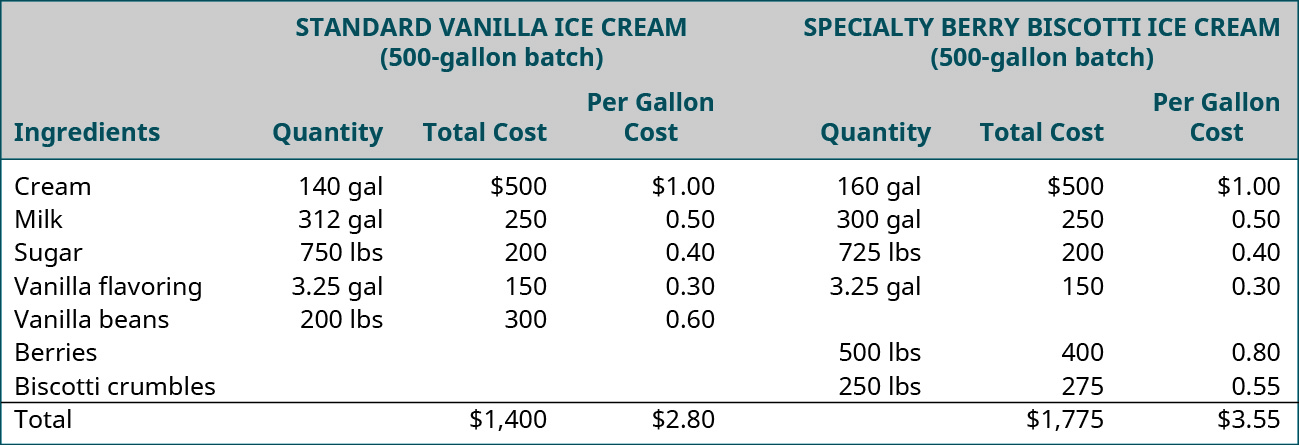
For example, Daryn'southward Dairy makes many different organic dairy products. Daryn's managers demand to track their costs for sure jobs. One of the company'south top-selling ice creams is their seasonal variety; a new flavor is introduced every iii months and sold for only a half dozen-month menstruation. The cost of these specialty water ice creams is different from the toll of the standard flavors for reasons such as the unique or expensive ingredients and the specialty packaging. Daryn wants to compare the costs involved in making the specialty ice cream and those involved in making the standard flavors of ice cream. This assay will crave that Daryn rail not only the cost of materials that go into the product, but also the labor hours and cost of the labor, plus other costs, known as overhead costs (rent, electricity, insurance, etc.), that are incurred in producing the various water ice creams. Once the total costs for both the specialty ice foam and the standard flavored ice cream are known, the toll per unit can be determined for each type. These types of analyses help a company evaluate how to set pricing, evaluate the demand for new or substitute ingredients, manage product additions and deletions, and make many other decisions. (Figure) shows an case of a materials cost analysis past Daryn's Dairy used to compare the materials cost for producing 500 gallons of their best-selling standard flavor—vanilla—with one of their specialty ice creams—Very Berry Biscotti.
Material Cost Analysis. Daryn's Dairy materials toll comparing analysis between acknowledged standard vanilla ice cream and Very Berry Biscotti, a limited-edition specialty ice cream. (attribution: Copyright Rice University, OpenStax, nether CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license)
Fiscal and Managerial Accounting Comparative
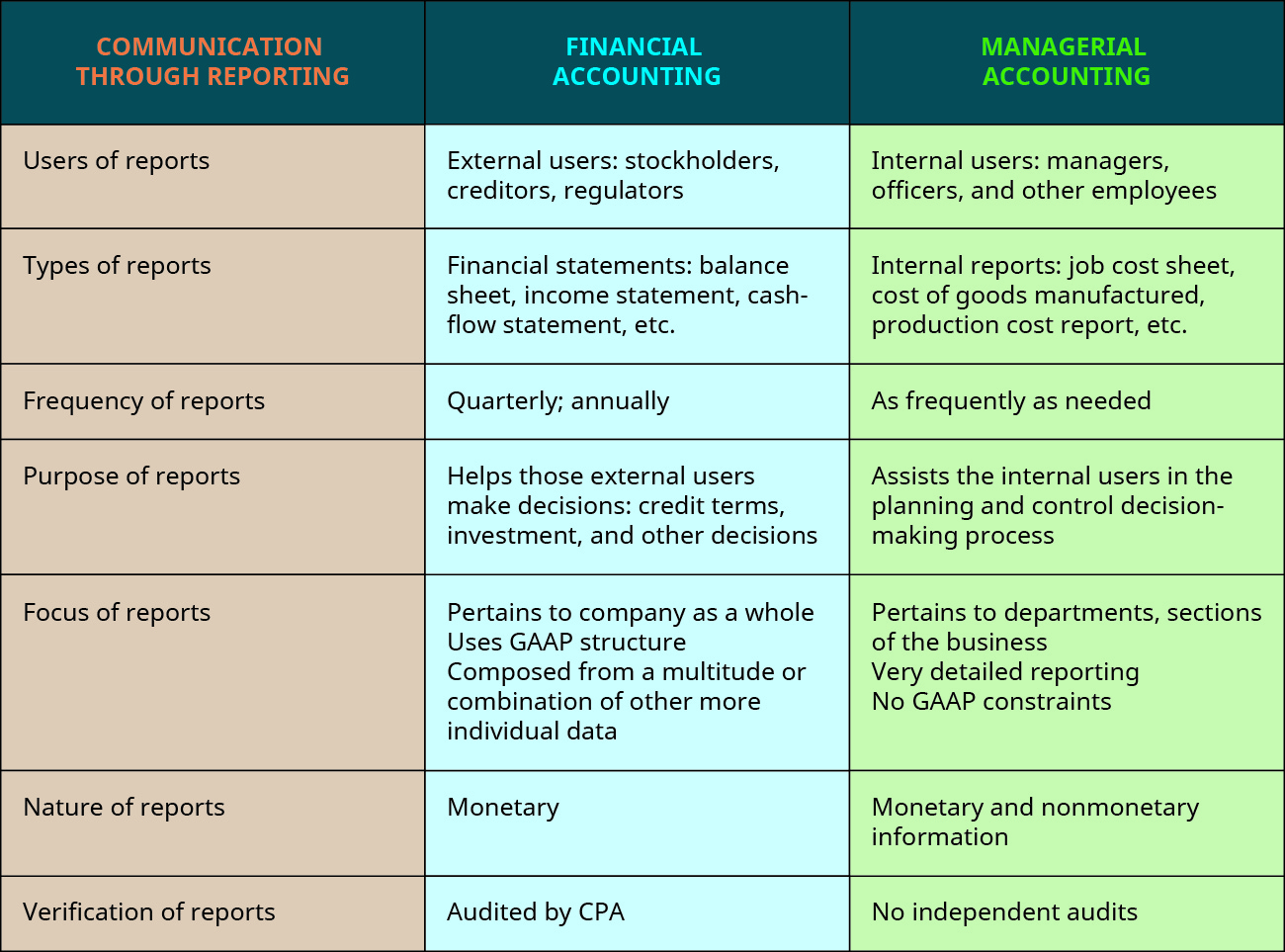
Managerial and financial accounting are used past every business, and there are of import differences in their reporting functions. Those differences are detailed in (Figure).
Comparing Reports between Financial and Managerial Bookkeeping. (attribution: Copyright Rice Academy, OpenStax, under CC By-NC-SA 4.0 license)
Users of Reports
The data generated from the reports of financial accountants tends to be used primarily by external users, including the creditors, tax authorities and regulators, investors, customers, competitors, and others outside the company, who rely on the financial statements and annual reports to admission data about a company in lodge to make more informed decisions. Since these external people do not have access to the documents and records used to produce the financial statements, they depend on Mostly Applied Bookkeeping Principles (GAAP). These outside users besides depend greatly on the preparation of audits that are done by public accounting firms, nether the guidelines and standards of either the American Constitute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA), the Usa Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), or the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB).
Managerial accounting information is gathered and reported for a more specific purpose for internal users, those inside the company or arrangement who are responsible for managing the company's concern interests and executing decisions. These internal users may include management at all levels in all departments, owners, and other employees. For case, in the upkeep development process, a visitor such as Tesla may desire to project the costs of producing a new line of automobiles. The managerial accountants could create a budget to approximate the costs, such equally parts and labor, and after the manufacturing process has begun, they can measure out the bodily costs, thus determining if they are over or nether their approaching amounts. Although outside parties might be interested in this information, companies like Tesla, Microsoft, and Boeing spend significant amounts of time and money to proceed their proprietary information hugger-mugger. Therefore, these internal budget reports are but available to the appropriate users. While y'all can find a cost of goods sold schedule in the financial statements of publicly traded companies, it is difficult for outside parties to break it down in order to place the individual costs of products and services.
Types of Reports
Fiscal accounting information is communicated through reporting, such as the fiscal statements. The fiscal statements typically include a balance sail, income statement, cash period statement, retained earnings statement, and footnotes. Managerial accounting information is communicated through reporting too. Nonetheless, the reports are more detailed and more than specific and can be customized. One case of a managerial accounting report is a budget analysis (variance study) as shown in (Figure). Other reports can include cost of goods manufactured, job social club cost sheets, and production reports. Since managerial accounting is not governed by GAAP or other constraints, it is important for the creator of the reports to disclose all assumptions used to brand the written report. Since the reports are used internally, and not typically released to the general public, the presentation of any assumptions does not have to follow whatsoever industry-wide guidelines. Each arrangement is free to structure its reports in the format that organizes its information in the all-time way for it.
Example of a Budget (Variance) Analysis. (attribution: Copyright Rice University, OpenStax, nether CC By-NC-SA 4.0 license)
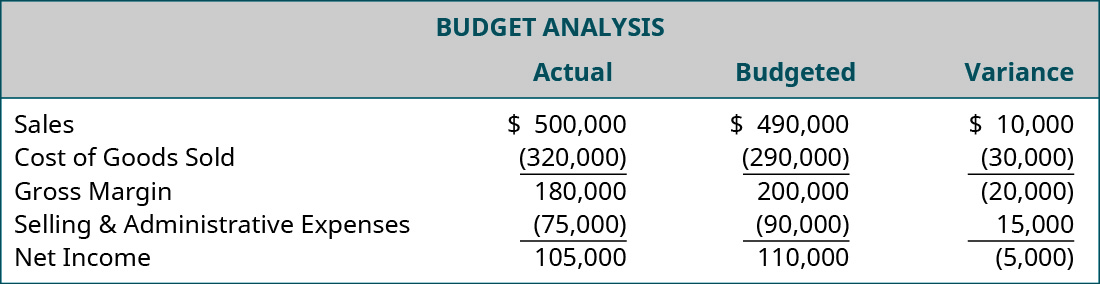
This type of analysis helps management to evaluate how effective they were at carrying out the plans and meeting the goals of the corporation. Y'all volition see many examples of reports and analyses that can be used as tools to help management brand decisions.
Projection Error
You are working as the auditor in the special projects and budgets area of Sturm, Ruger & Visitor, a law firm that currently specializes in defalcation police force. In order to serve their customers meliorate and more than efficiently, the company is trying to determine whether or not to expand its services and offer credit counseling, credit monitoring, credit rebuilding, and identity protection services. The president comes to you and asks for some sales and revenue projections. He would like the projections in three days' fourth dimension and so that he tin can present the results to the lath at the annual meeting.
You piece of work tirelessly for 2 directly days compiling projections of sales and revenues to prepare the reports. The report is provided to the president just before the board is to make it.
When y'all render to your office, you outset clearing away some of the materials that you used in your written report, and you discover an error that makes all of your projections significantly overstated. Y'all ask the president'due south authoritative assistant if the president has presented the report to the board, and you find that he had mentioned information technology but not given the total study as of yet.
What would you do?
- What are the upstanding concerns in this matter?
- What would exist the results of telling the president of your error?
- What would be the results of not telling the president of your error?
Frequency of Reports
The financial statements are typically generated quarterly and annually, although some entities likewise require monthly statements. Much work is involved in creating the financial statements, and whatever adjustments to accounts must be fabricated before the statements can be produced. A concrete count inventory must be done to suit the inventory and cost of goods sold accounts, depreciation must be calculated and entered, all prepaid asset accounts must be reviewed for adjustments, and then forth. The annual reports are non finalized for several weeks later the twelvemonth-end, considering they are based on historical data; for a company that is traded on one of the major or regional stock exchanges, it must have an audit of the financial statements conducted past an contained certified public accountant. This audit cannot exist completed until later on the finish of the visitor's fiscal yr, considering the auditors need admission to all of the information for the company for that yr. For companies that are privately held, an inspect is not normally required. However, potential lenders might require an independent audit.
Conversely, managers can apace attain managerial accounting information. No external, independent auditors are needed, and it is not necessary to look until the year-terminate. Projections and estimates are acceptable. Managers should understand that in club to obtain information quickly, they must have less precision in the reporting. While there are several reports that are created on a regular basis (e.chiliad., budgets and variance reports), many management reports are produced on an as-needed basis.
Purpose of Reports
The general purpose of financial argument reporting is to provide information near the results of operations, fiscal position, and cash flows of an organization. This data is useful to a wide range of users in guild to make economic decisions. The purpose of the reporting washed by management accountants is more specific to internal users. Direction accountants make available the information that could assistance companies in increasing their functioning and profitability. Unlike financial reports, management reporting centers on components of the business. By dividing the business organization into smaller sections, a company is able to get into the details and analyze the smallest segments of the business.
An agreement of managerial accounting volition aid anyone in the business world in determining and agreement product costs, analyzing intermission-even points, and budgeting for expenses and hereafter growth (which will be covered in other parts of this class). As a manager, chief executive officer, or possessor, you need to have information bachelor at paw to answer these types of questions:
- Are my profits college this quarter over last quarter?
- Practise I have enough greenbacks flow to pay my employees?
- Are my jobs priced correctly?
- Are my products priced correctly in society for me to brand the profit I demand to brand?
- Who are my most productive and to the lowest degree productive employees?
In the world of business organisation, information is power; stated but, the more you know, typically, the meliorate your decisions can exist. Managerial accounting delivers data-driven feedback for these decisions that can assist in improving decision-making over the long term. Business managers tin leverage this powerful tool in social club to brand their businesses more successful, because management accounting adds value to common business decision-making. All of this readily available information can lead to neat improvements for any business.
Focus of Reports
Because financial accounting typically focuses on the company equally a whole, external users of this information cull to invest or loan money to the entire company, not to a department or division inside the company. Therefore, the global focus of financial accounting is understandable.
However, the focus of management accounting is typically unlike. Managerial reporting is more focused on divisions, departments, or any component of a concern, down to individuals. The mid-level and lower-level managers are typically responsible for smaller subsets within the company.
Managers need accounting reports that bargain specifically with their division and their specific activities. For example, product managers are responsible for their specific area and the results within their division. Accordingly, these production managers need information about results achieved in their division, as well as individual results of departments within the segmentation. The company tin can be cleaved into segments based on what managers need—for example, geographic location, production line, customer demographics (eastward.k., gender, age, race), or whatever of a variety of other divisions.
Nature of Reports
Both financial reports and managerial reports use monetary accounting data, or information relating to money or currency. Financial reports utilize data from the bookkeeping organisation that is gathered from the reporting of transactions in the form of journal entries and so aggregated into fiscal statements. This information is monetary in nature. Managerial bookkeeping uses some of the same fiscal information equally financial accounting, but much of that information will be broken down to a more detailed level. For case, in fiscal reporting, net sales are needed for the income argument. In managerial accounting, the quantity and dollar value of the sales of each product are likely more useful. In improver, managerial bookkeeping uses a significant corporeality of nonmonetary bookkeeping information, such as quantity of textile, number of employees, number of hours worked, and and so forth, which does not relate to money or currency.
Verification of Reports
Financial reports rely on structure. They are generated using accepted principles that are enforced through a vast set of rules and guidelines, likewise known as GAAP. As mentioned previously, companies that are publicly traded are required to have their fiscal statements audited on an annual basis, and companies that are not publicly traded also may be required to accept their financial statements audited by their creditors. The data generated by the management accountants is intended for internal use by the visitor's divisions, departments, or both. At that place are no rules, guidelines, or principles to follow. Managerial accounting is much more flexible, so the design of the managerial accounting system is difficult to standardize, and standardization is unnecessary. It depends on the nature of the manufacture. Different companies (even dissimilar managers within the aforementioned company) require different information. The most important issue is whether the reporting is useful for the planning, controlling, and evaluation purposes.
Daryn's Dairy
Assorted Ice Cream Flavors. (credit: "Contrasted Ice Creams" past "jeshoots"/Pexel, CC0)

Suppose you lot have been hired by Daryn's Dairy as a market analyst. Your commencement assignment is to evaluate the sales of various standard and specialty ice creams within the Midwest region where Daryn's Dairy operates. You also demand to determine the all-time-selling flavors of ice cream in other regions of the United States as well as the selling patterns of the flavors. For instance, do some flavors sell better than others at unlike times of the year, or are some top sellers sold as express-edition flavors? Remember that one of the strategic goals of the company is to increase market share, and the first step in coming together this goal is to sell their product in x per centum more stores within their current market, so your research volition help upper-level management carry out the company's goals. Where would you gather the data? What type of information would y'all need? Where would you find this data? How would the company determine the impact of this type of change on the business? If implemented, what information would you lot need to appraise the success of the plan?
Solution
Answers volition vary. Sample answer:
Where would yous gather the information? Where would y'all detect this data?
- Electric current company sales data would be obtained from internal company reports and records that particular the sale of each type of ice foam including volume, toll, price, and profit per flavor.
- Sales of ice cream from other companies may be more than difficult to obtain, but the footnotes and supplemental information to the annual reports of those companies being analyzed, as well as industry trade journals, would likely be good sources of information.
What types of data would y'all need?
- Some of the types of data that would be needed would be the volume of sales of each flavor (number of gallons), how long each flavor has been sold, whether seasonal or limited-edition flavors are produced and sold simply once or are on a rotating basis, the size of the market being examined (number of households), whether the other companies sell similar products (organic, all natural, etc.), the median income of consumers or other information to assess the consumers' willingness to pay for organic products, and so forth.
How would Daryn's Dairy decide the bear on of this type of change on the business?
- Direction would evaluate the price to expand into new stores in their current market place compared to the potential revenues from selling their products in those stores in guild to assess the ability of the potential expansion to generate a profit for the company.
If implemented, what data would Daryn's Dairy demand to assess the success of the programme?
- Management would mensurate the profitability of selling any new products, expanding into new stores in their current market, or both to determine if the implementation of the plan was a success. If the program is a success and the visitor is generating profits, the company will continue to effigy out ways to improve efficiency and profitability. If the plan is not a success, the company will determine the reasons (cost to produce too high, sales price too loftier, volume too low, etc.) and make a new program.
Central Concepts and Summary
- Managerial bookkeeping provides information to managers and other users within the company. It has a specific focus, and the information is detailed and timely.
- Financial accounting follows the guidelines of the GAAP, gear up in place past the FASB and, in many cases, past the SEC. Managerial accounting is much more flexible and does not have to follow specific rules or guidelines.
- At that place are seven key differences between managerial accounting and financial accounting: users, types of reports produced, frequency of producing the reports, purpose of the information produced, focus of the reporting information, nature of the original information used to produce the reports, and verification of the data used to create the reports.
(Figure)Managerial bookkeeping produces information:
- to meet the needs of external users
- that is often focused on the future
- to see the needs of investors
- that follows the rules of GAAP
(Figure)Management accounting:
- emphasizes special-purpose data
- relates to the company every bit a whole
- is limited to strictly cost figures
- is controlled past GAAP
(Figure)Internal users of accounting information would non include ________.
- managers
- employees
- creditors
- officers
(Figure)External users of bookkeeping information would include ________.
- employees
- managers
- investors
- supervisors
(Figure)Which of the following statements is incorrect?
- The practice of management accounting is fairly flexible.
- The information gathered from management bookkeeping is not required past law.
- Management bookkeeping focuses mainly on the internal user.
- Reports produced using direction accounting must follow GAAP.
(Figure)How exercise the discipline matter of reports and the verification of reports differ between financial accounting and managerial bookkeeping?
Reports generated from financial bookkeeping are a compilation of a company's various transactions and contain aggregated data for the entire company in the course of financial statements. For publicly traded companies, these reports follow the rules set forth past the Fiscal Accounting Standards Board (FASB). In addition, the financial statements are verified by external auditors. Reports generated by managerial accounting are varied in nature considering they are driven by the questions that need to be addressed by management. Different companies and different questions require different reports. Managerial accounting reports are therefore on a more detailed level, such every bit on a product or sectionalization level. At that place are no specific rules guiding the cosmos of these reports, and they are usually unaudited.
(Figure)What is the purpose of direction accounting?
(Figure)Who are the primary users of the information gathered past managerial accountants?
The primary users of information gathered past managerial accountants are internal users, including management, employees, and officers.
(Effigy)What are the key differences between financial bookkeeping and managerial bookkeeping?
(Effigy)Signal whether each argument describes financial accounting or managerial accounting.
- The data is directed at external users who are making decisions pertaining to investing, extending credit, and other decisions.
- The principal users are the organization's managers.
- The cardinal focus is on the entity equally a whole.
- The rules and principles are very flexible.
- The information gathered is commonly bachelor after an independent audit has been completed.
(Figure)Identify the following equally True or Faux:
- Managerial bookkeeping reports must comply with the rules set in identify by the FASB.
- Financial accounting reports are typically general-purpose reports.
- Financial accounting reports pertain to the entity as a whole, whereas managerial accounting focuses more on subunits of the organization.
- The main users of the financial accounting information are the internal users.
- Managerial reports are prepared on an as-needed basis.
- Financial accounting reports often must exist audited at to the lowest degree annually by an independent auditor.
(Figure)Define each of these users of bookkeeping information as an internal user of external user:
- Management
- Employees
- Investors
- Creditors
- Customers
- Tax authorities
(Figure)Hash out what data would be most useful for these users of accounting information:
- Management
- Employees
- Investors
- Creditors
- Customers
- Tax authorities
(Figure)Indicate whether the argument describes reporting past the financial bookkeeping part or the managerial accounting function of an system.
- The users of the study are managers who demand a daily summary of work done each shift.
- The study is a job cost canvas for jobs completed in a 24-hour menstruum.
- The annual report is released each year on the company'due south website.
- The written report is audited past the company'southward certified public accountant house.
- The study is prepared every 24-hour interval considering the customer service managing director needs information about inventory fix to be shipped to customers.
(Figure)Identify the post-obit every bit true or false:
- Financial bookkeeping reports are not released to external users.
- Managerial accounting reports are not used by employees inside the organization.
- Managerial bookkeeping reports include only monetary information.
- Financial accounting reports are monetary in nature.
- If a result of a visitor's operations is nonmonetary in nature, it must exist converted to monetary units for managerial reporting.
- Tax government and government regulatory agencies are external users of financial information.
(Figure)Companies demand to report both monetary and nonmonetary information and information.
- Ascertain these 2 terms and provide examples of each.
- Discuss what sources are bachelor that provide companies with both types of data and information.
Glossary
- external user
- someone who relies on the financial statements and almanac reports to access information about a company in order to make more than informed decisions (e.g., creditor, tax say-so and regulator, investor, customer, competitor, and others)
- Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB)
- independent, nonprofit organization that sets financial accounting and reporting standards for both public and private sector businesses in the The states that use Mostly Accepted Bookkeeping Principles (GAAP)
- generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP)
- common set of rules, standards, and procedures that publicly traded companies must follow when composing their financial statements
- internal user
- someone inside the visitor or system who is responsible for managing the visitor'south business interests and executing decisions (due east.g., all levels of management, possessor, and other employees)
- monetary bookkeeping information
- relating to money or currency
- nonmonetary accounting information
- not relating to coin or currency, such every bit the quantity of materials, number of employees, number of hours worked, and so forth
Source: https://opentextbc.ca/principlesofaccountingv2openstax/chapter/distinguish-between-financial-and-managerial-accounting/
Postar um comentário for "Which of the Following Applies to Where a Managerial Accounting System Can Be Useful?"